Rose of Sharon (Hibiscus syriacus)
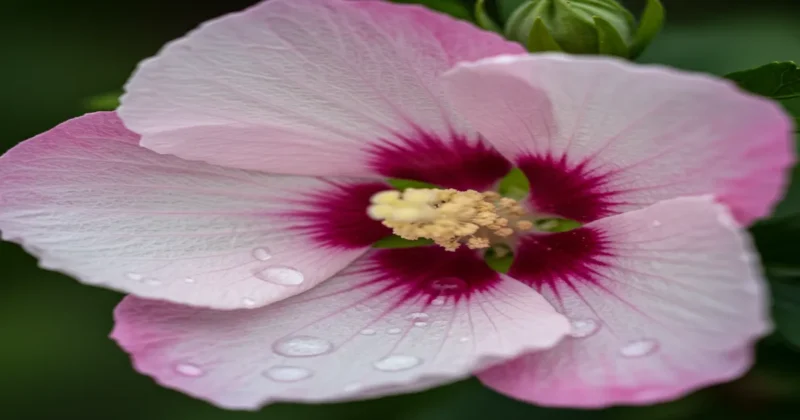
Rose of Sharon (Hibiscus syriacus) is a type of hibiscus that sheds its leaves and features dark green foliage, producing many eye-catching blooms during the summer and fall seasons. The flowers, resembling paper, have five petals and can grow up to 3 inches in diameter. They come in various colors and bicolors, appearing as either single or frilly double blooms.
It is classified as a shrub, developing an upright vase shape with multiple branches that can also be pruned to form a single trunk. Rose of Sharon is a plant that requires minimal upkeep, is tolerant to drought and heat, and can adapt to unfavorable soil and urban environments. It typically lives for 20 to 30 years.
Planting Rose of Sharon
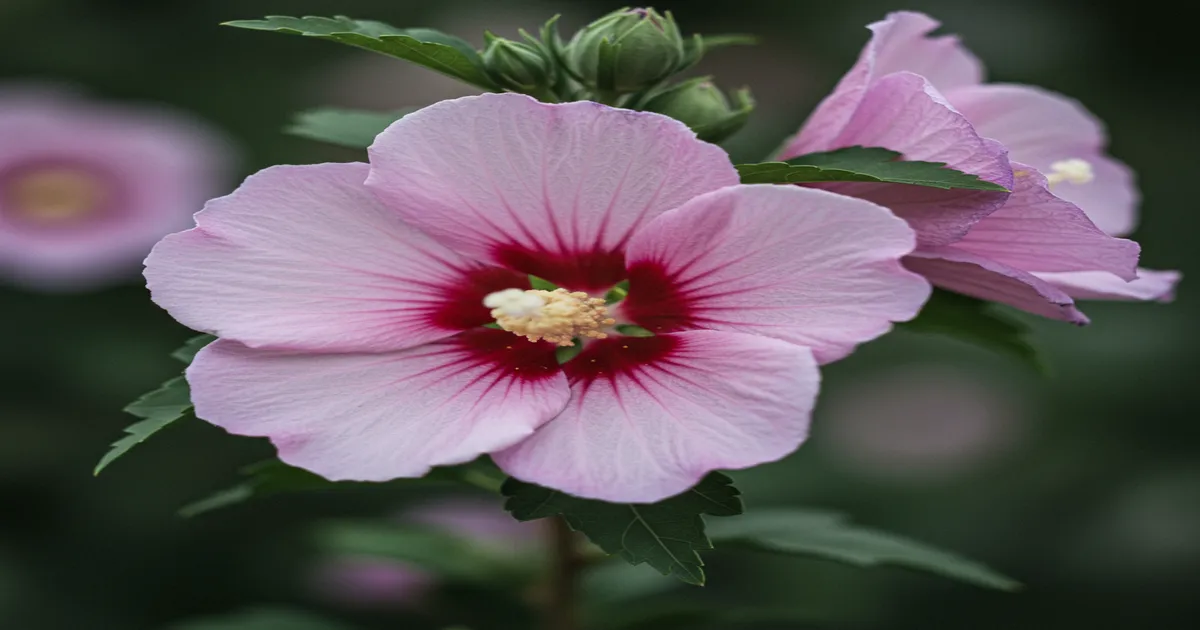

Rose of Sharon should be planted after the final spring frost in regions with cold winters. In southern climates, it can be planted in late fall. For optimal flowering, choose a location with full sun exposure of 6 to 8 hours daily. While Rose of Sharon cannot thrive in boggy soil, it can adapt to poor soil as long as it is well-draining. Follow these steps for planting.
Varieties of Rose of Sharon
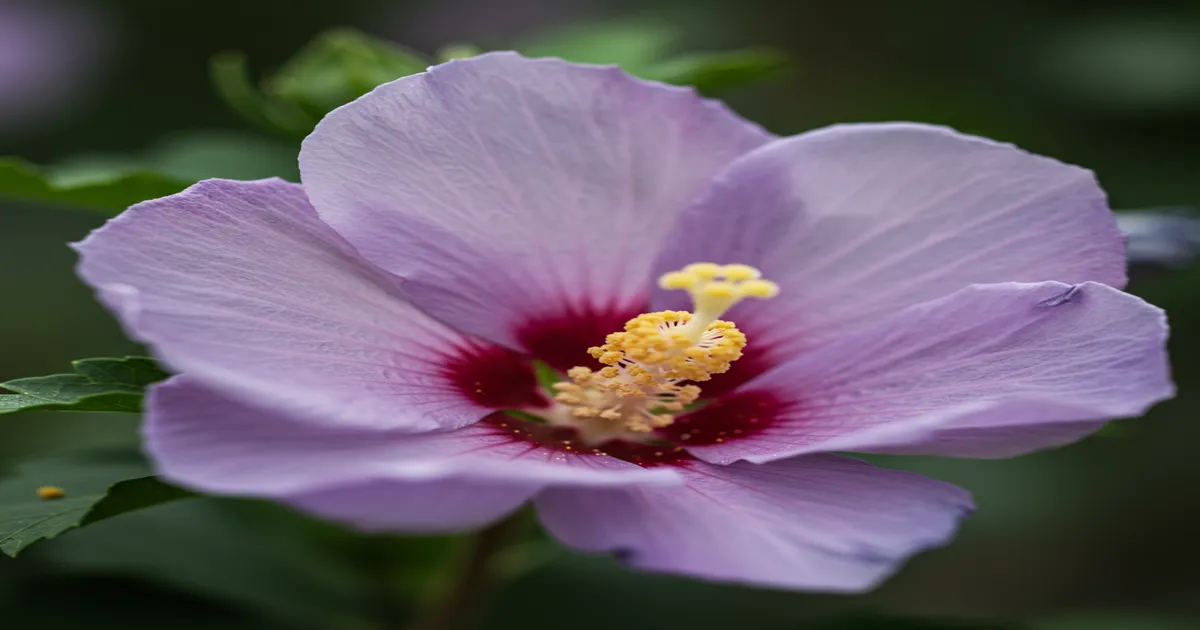

The following are some popular types of Rose of Sharon:
- ‘Blue Chiffon’: This type features double flowers (two layers of petals) in a purple-blue shade that blossom from mid-summer to autumn. It reaches a height of 8′ to 12′ with a width of 6′ to 10′.
- ‘Sugar Tip’: This variety is named for its variegated leaves edged in creamy-white. It produces pink double flowers and grows 6′ to 8′ tall and 4′ to 6′ wide.
- ‘White Chiffon’: This type showcases pure white flowers without a contrasting throat. It grows 6′ to 8′ tall and 4′ to 6′ wide.
- ‘Red Heart’: This shrub bears ruffled flowers with white petals and dark red centers. Gardeners who prefer low-maintenance landscaping will appreciate that this is a sterile cultivar, meaning it won’t generate any unwanted seedlings.
Landscaping Ideas With Rose of Sharon
- Plant compact varieties in pots as ‘thrillers.’
- Establish a hedge or barrier with a single type or various varieties of the same size.
- Use as part of a foundation planting.
- Incorporate as a tall background plant in flowerbeds.
Trimming

Rose of Sharon produces flowers on new growth, therefore it is best to trim in late winter or early spring. Trimming the tips of the stems will promote branching and flowering. Prune any damaged or diseased branches as needed.
Remove spent rose of Sharon flowers that are self-seeding before they form seeds. This practice reduces undesired spreading and assists in managing the plant’s invasive tendencies.
How to Propagate Rose of Sharon

The most effective method for propagating this shrub is through stem cuttings. This approach not only offers a cost-effective way to create a new plant but also enables you to preserve the lineage of a particular variety with flowers you especially enjoy. The optimal time for taking cuttings is in midsummer. Here is a step-by-step guide:
Steps for Propagating Rose of Sharon From Seeds
Rose of Sharon plants can easily spread seeds on their own in the garden, but you can also plant the seeds yourself.
Transferring Rose of Sharon to a New Pot
When potting or repotting a rose of Sharon, it is best to do so during warmer temperatures, such as in the spring or fall. Avoid using a pot that is too large; instead, select one that is only one to three inches bigger than the plant’s roots.
Rose of Sharon thrives in well-draining soil, so it is essential to use a pot with drainage holes and high-quality potting mix. As the plant matures, you can either move it to a larger pot or trim the roots.
Winter Protection
Rose of Sharon generally doesn’t require specific winter maintenance within its hardiness zones. It’s best to place it in a location shielded from harsh, cold, drying winds. If you reside in a colder region of its hardiness zones, applying a layer of mulch around the base can also provide insulation for the shrub during severe weather conditions.
Types of Common Pests
The primary pest issue that affects this shrub is the Japanese beetle. These beetles are relatively easy to manage compared to other insects because of their noticeable large size. This means you are likely to detect them before they cause significant harm to your plant.
The most straightforward method to eliminate them is to manually pick or shake them off the plant and place them in a container with soapy water. Since the insect breathes through its skin, covering it with soap suffocates it effectively.
Tips for Getting Rose of Sharon to Flower
Rose of Sharon will bloom consistently year after year when exposed to full sun and provided with sufficient moisture. The flowers attract bees, butterflies, hummingbirds, and other pollinators.
Flowering Period
Rose of Sharon usually blooms from spring to fall. Pruning in late winter will ensure abundant blooming during the warmer months.
Duration of Blooms
The flowers of Rose of Sharon are short-lived, lasting from one to three days. Blooming frequently is encouraged by full sun exposure.
Appearance and Scent of Rose of Sharon Flowers
The flowers resemble tropical hibiscus blossoms with five papery petals and prominent stamens. They can be single or double, with many varieties featuring a contrasting throat. The fragrance is a delicate, floral perfume.
Promoting Abundant Blooms
Prune Rose of Sharon in late winter and ensure it is planted in full sun to enjoy continuous flowering throughout the season.
Removing Spent Rose of Sharon Blooms
Once the blooming period of Rose of Sharon ends, remove the spent flowers before seed pods form. This practice prevents the shrub from spreading, especially in regions where it is considered invasive.
Lack of Blooms
Various factors can lead to poor or nonexistent blooming of the shrub. Late pruning in spring may accidentally remove flower buds. Additionally, drought conditions can cause Rose of Sharon to stop flowering, so it’s essential to provide supplemental water during hot and dry spells.
Moreover, a phosphorus-deficient soil can reduce flower production and result in smaller blooms. Conduct a soil test to identify any deficiencies and apply fertilizer as required.